The majestic artichoke stands as a remarkable example of the natural world’s complexity and beauty. Originating from the thistle family, the artichoke offers a unique blend of textures, flavors, and nutrients, making it a favorite among food enthusiasts and gardeners alike.
Unraveling the mysteries of the anatomy of an artichoke not only enhances our appreciation of this vegetable but also guides us in its culinary preparation. Let’s delve into the intricate world of the artichoke’s structure and discover what makes it both fascinating and delicious.
Anatomy of an Artichoke: Labeled
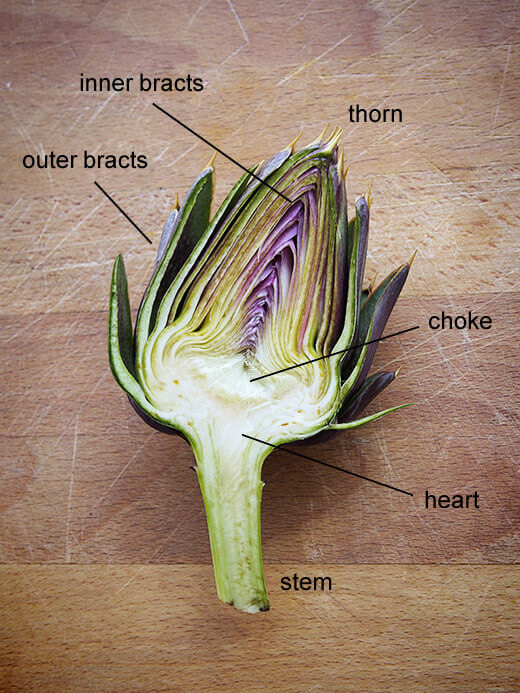
The anatomy of an artichoke is more intricate than one might expect from its humble appearance. At its core lies the artichoke heart, encased by a series of protective petals known as bracts. As we dissect the anatomy further, we encounter the choke, the stem, and the base, each playing a crucial role in the artichoke’s development and culinary use.
The artichoke’s external bracts, though tough, are essential in safeguarding the tender heart within. These bracts gradually become more edible as they approach the base, offering a range of textures to be enjoyed. The stem, often overlooked, is an extension of the heart and carries a similar flavor profile, making it worthy of inclusion in many recipes.
- Heart: The succulent center prized for its flavor.
- Bracts: Petal-like components protecting the heart.
- Choke: Fuzzy fibers atop the heart, often removed.
- Stem: Edible extension of the heart.
- Base: The foundation from which the bracts and heart emerge.
A thorough understanding of this structure is invaluable when preparing an artichoke for cooking, ensuring that one can utilize the vegetable to its fullest potential.
What Is an Artichoke?
An artichoke is a unique plant, both a vegetable and a flower bud, hailing from the thistle plant known scientifically as Cynara cardunculus. It boasts an impressive stature, with mature specimens reaching significant widths and heights.
When examining the detailed anatomy of an artichoke, it’s clear that the vegetable we consume is actually the bud before it blooms into its full floral form. This premature stage allows us to enjoy the artichoke’s distinctive taste and texture, which might otherwise be lost once flowering occurs.
Artichokes are not just a culinary delight but also a source of nourishment, as artichoke heart benefits include a rich supply of antioxidants and fiber. This combination of utility and nutritional value makes the artichoke a laudable addition to any diet.
Is Artichoke a Flower?
The artichoke is indeed a flower in waiting. If left to grow unchecked, the artichoke flower bud will blossom into a striking blue-violet flower. This transformation, while beautiful, renders the bud inedible, hence the importance of timely harvesting.
The relationship between the artichoke and its flowering phase is a testament to the dynamic nature of plants. Understanding this process is essential for both gardeners and chefs, as it influences the timing of harvesting and the quality of the artichokes produced.
What Part of the Artichoke Is Poisonous?
While the artichoke is a delight to the palate, one must approach its preparation with care. The poisonous part of the artichoke is not a concern when dealing with the edible varieties commonly found in markets; however, it is the thorns on the outer bracts that can pose a risk if not handled properly.
These thorns require careful removal during preparation to avoid injury. It’s a small but crucial consideration that ensures the safe consumption and enjoyment of this otherwise benign and wholesome vegetable.
What Does an Artichoke Heart Taste Like?
The artichoke heart is the crowning jewel of the vegetable, boasting a taste that’s both nutty and subtly sweet. This flavor profile is complemented by a buttery texture that makes the artichoke heart a versatile ingredient in a myriad of dishes.
Whether enjoyed on its own, as part of a dip, or within a more complex recipe, the artichoke heart’s taste is distinct and memorable. It’s a gourmet experience that encapsulates the essence of the vegetable’s appeal.
Anatomy of an Artichoke Leaves
The leaves of an artichoke, or bracts, serve as a protective barrier that gradually becomes edible as they near the base. Their taste and texture transition from tough and bitter to tender and flavorful, inviting a layered gastronomic journey from the outside in.
These bracts are not only significant in taste but also in nutrient content, offering dietary fiber and antioxidants. The art of consuming artichoke leaves is a time-honored tradition that maximizes the vegetable’s culinary potential.
Artichoke leaves can be enjoyed in a variety of ways, often involving a ritualistic approach to peeling and dipping, which adds to the overall dining experience. This interactive element is one of many charms that the artichoke extends to those who take the time to savor it in its entirety.
Anatomy of an Artichoke Heads
The term “head” of an artichoke is commonly used but can be misleading. In botanical terms, the “head” refers to the entire flower bud, which is composed of numerous bracts and the precious heart within. It’s this collective structure that is harvested and consumed.
The head is where the essence of the artichoke’s flavor and nutrition resides. It’s a complex assembly of parts, each contributing to the overall character of the vegetable. Understanding the head’s anatomy is essential for those seeking to master the preparation and enjoyment of artichokes.
Artichoke heads can be intimidating due to their protective thorns and fibrous choke, but with knowledge and skill, these challenges are easily overcome. The reward is a culinary treasure that’s as nourishing as it is delightful.
Related Questions on Artichoke Anatomy
What is an artichoke?
An artichoke is a type of thistle plant that produces a large, edible flower bud. It is both a dietary staple and a culinary delicacy, loved for its unique flavor and texture. The edible components are primarily the artichoke heart, the base of the stems, and the lower parts of the bracts or leaves.
Cultivated as a food source for centuries, the artichoke is rich in nutrients, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Its cultivation and harvesting have been refined over time, ensuring that we enjoy this vegetable in its prime state.
Is artichoke a flower?
Yes, the artichoke is, in essence, an immature flower. It is the bud of a flowering plant that, if allowed to mature, would bloom into an eye-catching flower. The stage at which artichokes are typically harvested is crucial, as it determines the quality and edibility of the bud.
Understanding the artichoke’s place in the floral world highlights its uniqueness among vegetables and its beauty as a natural creation.
What part of the artichoke is poisonous?
There is no inherently poisonous part of the artichoke when it comes to the varieties cultivated for consumption. However, the tips of the leaves contain thorns which can cause physical harm if not handled correctly. It’s important to remove these before preparing or eating the artichoke.
With proper preparation, all parts of the artichoke can be safely enjoyed, with no risk of poisoning from the plant itself.
What does an artichoke heart taste like?
The artichoke heart is often described as having a rich, nutty, and slightly sweet flavor. Its texture is tender and meaty, making it a versatile ingredient that can be used in various culinary applications. The unique taste of the artichoke heart is what makes it so prized among chefs and food enthusiasts.
Whether sautéed, grilled, or served in a creamy dip, the artichoke heart is a component that adds depth and sophistication to any dish.
Anatomy of an artichoke labeled?
When labeling the anatomy of an artichoke, one typically identifies the following parts: the heart, the choke (a mass of immature florets), the bracts (sometimes referred to as leaves), the stem, and the base from which all other parts grow. Each component plays a pivotal role in the artichoke’s development and culinary value.
Understanding the labeled anatomy allows for a greater appreciation of the artichoke’s complexity and aids in its preparation and presentation in dishes.
For a visual guide to the artichoke’s structure, let’s turn to an informative video from Ocean Mist Farms:
As we explore the wonders of the artichoke, we are reminded of the intricate connections between form, function, and flavor within the natural world. The artichoke, with its complex anatomy and delightful taste, stands as a testament to the diversity and ingenuity of edible plants.